
Pure Titanium Powder
Overview of Pure Titanium Powder Titanium powder is a metal powder made from titanium metal. It is characterized by its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Titanium powder has diverse applications across industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and consumer products. This article provides a comprehensive guide to titanium powder. It covers the composition,…
Piccolo MOQ
Sourcing flessibile per centinaia di prodotti
Supporto alla personalizzazione
Polvere personalizzata in base all'industria
Spedizione rapida
Con DHL Express, sicuro e veloce direttamente nelle vostre mani
Overview of Pure Titanium Powder
Titanium powder is a metal powder made from titanium metal. It is characterized by its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Titanium powder has diverse applications across industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and consumer products.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to titanium powder. It covers the composition, properties, applications, specifications, suppliers, handling, inspection, comparisons, pros and cons, and frequently asked questions about titanium powder. Quantitative data is presented in easy-to-read tables for quick reference.
Composition of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder can be pure titanium or an alloy containing titanium as the main element. The composition determines the properties and applications.
| Composizione | Dettagli |
|---|---|
| Titanio puro | Contains >99% titanium. Lowest strength but excellent corrosion resistance. |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 6% aluminum, 4% vanadium. Most common titanium alloy with high strength. |
| Ti-3Al-2,5V | 3% aluminum, 2.5% vanadium. Higher ductility than Ti-6Al-4V. |
| Ti-6Al-7Nb | 6% aluminum, 7% niobium. Higher strength for aerospace applications. |
| Ti-15Mo-3Nb-3Al-0.2Si | 15% molybdenum, 3% niobium, 3% aluminum, 0.2% silicon. Beta titanium alloy. |
Titanium powder can also be blended with other elemental powders like iron, aluminum, or boron to create customized alloys.
Properties of Titanium Powder
The unique properties of titanium make it suitable for demanding applications across industries.
| Proprietà | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| elevata resistenza | Has excellent strength-to-density ratio, close to high strength steels. |
| Bassa densità | Weighs 60% less than steel or nickel alloys. |
| Resistenza alla corrosione | Forms stable TiO2 oxide film for corrosion protection. |
| biocompatibilità | Non-toxic and compatible with human body tissues. |
| Resistenza al calore | Maintains mechanical properties up to 600¡«C. |
| Non magnetico | Useful for non-magnetic applications. |
| Non-sparking | Safer for flammable environments compared to steel. |
The properties can be tuned by changing the composition, grain size, porosity, and processing method.
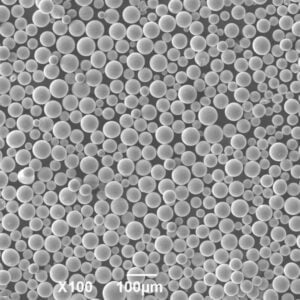
Applicazioni della polvere di titanio
The versatile properties of titanium powder enable unique applications in the following industries:
| Industria | APPLICAZIONI |
|---|---|
| Aerospaziale | Engine components, aircraft structures, space vehicles |
| Medico | Implants, surgical instruments, medical devices |
| Automotive | Connecting rods, valves, springs, fasteners |
| Chimico | Corrosion resistant vessels, heat exchangers, pipes |
| Sporting goods | Golf clubs, tennis rackets, bicycles, helmets |
| manifattura additiva | Aerospace, automotive, and medical 3D printed parts |
Titanium’s biocompatibility makes it ideal for implants and medical devices. Its corrosion resistance suits it for seawater applications. The high strength is useful for critical components in aerospace.
Specifiche della polvere di titanio
Titanium powder is available in different size ranges, shapes, purity levels, and composition to suit specific applications.
| Parametro | Specifiche tecniche |
|---|---|
| Dimensioni delle particelle | 15-45 microns, 45-105 microns, 105-250 microns |
| Forma delle particelle | Spherical, angular, mixed morphology |
| Purezza | Grade 1 (99.2% Ti), Grade 2 (99.5% Ti), Grade 4 (99.9% Ti) |
| Alloy grades | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-7Nb, Ti-64, Ti-1023 |
| Metodo di produzione | Gas atomization, plasma atomization, hydride-dehydride |
The particle size distribution, morphology, oxygen/nitrogen content, and microstructure are controlled as per application requirements.
Suppliers of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder is supplied by leading metal powder manufacturers globally:
| Fornitore | Ubicazione |
|---|---|
| AMETEK | USA |
| AP&C | Canada |
| Tecnologia TLS | Germania |
| Tekna | Canada |
| Metalysis | GB |
| Praxair | USA |
| Rio Tinto | Canada |
| ATI Powder Metals | USA |
| Gruppo Powder CNPC | Cina |
Titanium powder prices range from $50/kg to $500/kg based on purity, particle size, production method, and order volume. Custom alloys, special particle morphologies, and strict tolerances cost more.
Handling and Storage of Titanium Powder
Special precautions are needed when handling titanium powder to prevent fires, explosions, and property damage:
- Store in cool, dry, inert environments away from moisture, sparks, and flames
- Use conductive containers grounded to prevent static charge buildup
- Local exhaust ventilation is recommended to control dust
- Avoid dust accumulation to minimize explosion hazard
- Wear dust masks, safety goggles, gloves to prevent inhalation and skin contact
- Follow material safety data sheet (MSDS) instructions for safe handling
Inspection and Testing of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder batches are tested to ensure they meet the required material specifications:
| Metodo di Test | Parameter Measured |
|---|---|
| Analisi granulometrica | Distribuzione granulometrica |
| Diffrazione del laser | Particle size distribution, mean size |
| Microscopia elettronica a scansione | Particle morphology, microstructure |
| Spettroscopia di raggi X con energia dispersiva | Composizione chimica |
| Diffrazione dei raggi X | Phase composition |
| Spectrophotometry | Oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen content |
| Densità del materiale compattato | Apparent density, flowability |
| Pycnometer | Skeletal density |
Sampling and testing as per ASTM standards ensures titanium powder quality for critical applications.
Comparing Titanium Powder to Alternatives
Titanium has advantages and disadvantages compared to substitute materials:
| Titanio | Alluminio | Acciaio inox | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Densità | Scarso | Inferiore | Più alto |
| Forza | Elevato | Intermedio | Elevato |
| Resistenza alla corrosione | Eccellente | Bene | Bene |
| Temperature resistance | Bene | Intermedio | Migliore |
| Costi | Elevato | Scarso | Intermedio |
| Magnetic permeability | Scarso | Scarso | Elevato |
| biocompatibilità | Eccellente | Scarso | Bene |
Titanium stands out for its corrosion resistance and biocompatibility despite its higher cost. Aluminum and stainless steel may be cheaper alternatives depending on application requirements.
Pros and Cons of Titanium Powder
| * Alta densità: maggiore capacità di archiviazione in un fattore di forma più piccolo * Bassa latenza: tempi di accesso più rapidi rispetto ai dischi rigidi tradizionali * Elevata larghezza di banda: velocità di trasferimento dati più elevate * Maggiore affidabilità: meno parti mobili rispetto ai dischi rigidi tradizionali, riducendo il rischio di guasti * Maggiore efficienza energetica: consumo energetico inferiore rispetto ai dischi rigidi tradizionali * Silenzioso: nessun rumore di ricerca o rotazione | Contro |
|---|---|
| Elevato rapporto resistenza-peso | Expensive compared to steels |
| Resistente alla corrosione | Reactivity with oxygen at high temperatures |
| Non tossico e anallergico | Low elastic modulus can mean springback in machining |
| Eccellente biocompatibilità | Low thermal conductivity |
| Mantiene le proprietà ad alte temperature | Requires inert atmosphere processing |
| Wide range of alloying possibilities | Limited high temperature strength |
Titanium powder enables lightweight, strong parts but requires controlled handling and processing. Cost is higher than conventional alloys.
Frequently Asked Questions about Titanium Powder
Here are answers to some common questions about titanium powder:
Q: What is titanium powder used for?
A: Titanium powder has uses across aerospace, medical, automotive, chemical, and sporting goods due to its high strength, low weight, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and biocompatibility. It is commonly used for critical rotating parts in aircraft engines, orthopedic implants, automotive components, heat exchangers, and additively manufactured parts.
Q: Is titanium powder safe to handle?
A: Titanium powder can ignite and explode when very finely divided and exposed to air. Proper grounding, inert atmosphere, ventilation, and protective equipment are essential when handling titanium powder. It is also non-toxic and hypoallergenic on skin contact.
Q: What is the difference between Grade 1 and Grade 5 titanium powder?
A: Grade 1 titanium powder has higher purity with lower oxygen and iron content compared to Grade 5. Grade 1 provides better corrosion resistance while Grade 5 offers higher strength. Grade 5 powder would be used where strength is critical while Grade 1 suits chemical resistance needs.
Q: Does titanium powder rust?
A: Titanium forms an impervious and self-repairing oxide layer that protects it from rusting and corrosion. It exhibits excellent corrosion resistance in most environments including saltwater. This property makes it suitable for marine applications.
Q: Is titanium powder magnetic?
A: No, titanium powder is non-magnetic. Its relative magnetic permeability is very close to 1 which makes it useful for non-magnetic applications instead of ferritic steels.
Q: What is the cost of titanium powder?
A: Titanium powder can range from $50/kg to $500/kg depending on purity, particle size, production method, morphology, and order volume. High purity grades suitable for medical use are more expensive. Custom alloys and special particle shapes also cost more.
Q: What is the difference between gas atomized and hydride-dehydride titanium powder?
A: Gas atomized titanium powder has a spherical morphology ideal for additive manufacturing while hydride-dehydride powder has an angular, irregular shape suited for pressing-and-sintering. The powder properties, surface chemistry, microstructure and cost differ for the two production methods.
Q: How is titanium powder produced?
A: The main production methods are gas atomization, plasma atomization, and hydride-dehydride process. Gas atomization using argon or nitrogen gas is a common method to produce fine spherical powder for AM. The hydride process generates angular powder for pressing into shapes before sintering. Plasma atomization can produce very fine spherical powders.
Q: What are the contents of a titanium powder material safety data sheet (MSDS)?
A: The MSDS will have health hazard information, reactivity data, toxicological data, handling precautions, storage information, spill procedures, firefighting instructions, first aid measures, and disposal guidelines. It is critical to review the MSDS before working with any amount of titanium powder.
Q: What standards apply to titanium powder?
A: Key standards include ASTM B833 for spherical titanium powder, ASTM B981 for titanium alloys for powder metallurgy, ASTM B988 for gas atomized titanium alloy powder, and ISO 22068 for additive manufacturing with titanium alloys. The specifications cover sampling, testing, size analysis, chemical analysis, and quality assurance.
Contattateci ora
Contattateci per conoscere le ultime quotazioni dei prodotti e la disponibilità a magazzino.
