
순수 티타늄 분말
순수 티타늄 분말 개요 티타늄 분말은 티타늄 금속으로 만든 금속 분말입니다. 높은 중량 대비 강도, 내식성, 생체 적합성이 특징입니다. 티타늄 분말은 항공우주, 의료, 자동차, 소비재 등 산업 전반에 걸쳐 다양한 용도로 사용됩니다. 이 문서에서는 티타늄 분말에 대한 종합적인 가이드를 제공합니다. 이 글에서는 티타늄 분말의 구성,...
소량 주문 가능 (Small MOQ)
수백 개의 제품에 대한 유연한 조달
맞춤화 지원
산업에 따른 맞춤형 분말
Certainly! The translation of "Rapid shipment" to Korean is: 신속한 배송 (Shinsokhan Baesong)
DHL Express로 안전하고 빠르게 직접 손에 전달합니다.
Overview of Pure Titanium Powder
Titanium powder is a metal powder made from titanium metal. It is characterized by its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Titanium powder has diverse applications across industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and consumer products.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to titanium powder. It covers the composition, properties, applications, specifications, suppliers, handling, inspection, comparisons, pros and cons, and frequently asked questions about titanium powder. Quantitative data is presented in easy-to-read tables for quick reference.
Composition of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder can be pure titanium or an alloy containing titanium as the main element. The composition determines the properties and applications.
| 컴포지션 | 상세 정보 |
|---|---|
| 순수 티타늄 | Contains >99% titanium. Lowest strength but excellent corrosion resistance. |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 6% aluminum, 4% vanadium. Most common titanium alloy with high strength. |
| Ti-3Al-2.5V | 3% aluminum, 2.5% vanadium. Higher ductility than Ti-6Al-4V. |
| Ti-6Al-7Nb | 6% aluminum, 7% niobium. Higher strength for aerospace applications. |
| Ti-15Mo-3Nb-3Al-0.2Si | 15% molybdenum, 3% niobium, 3% aluminum, 0.2% silicon. Beta titanium alloy. |
Titanium powder can also be blended with other elemental powders like iron, aluminum, or boron to create customized alloys.
Properties of Titanium Powder
The unique properties of titanium make it suitable for demanding applications across industries.
| 부동산 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 강도 높음 | Has excellent strength-to-density ratio, close to high strength steels. |
| 저밀도 | Weighs 60% less than steel or nickel alloys. |
| 내식성 | Forms stable TiO2 oxide film for corrosion protection. |
| 생체적합성 | Non-toxic and compatible with human body tissues. |
| 내열성 | Maintains mechanical properties up to 600¡«C. |
| 비자석 | Useful for non-magnetic applications. |
| Non-sparking | Safer for flammable environments compared to steel. |
The properties can be tuned by changing the composition, grain size, porosity, and processing method.
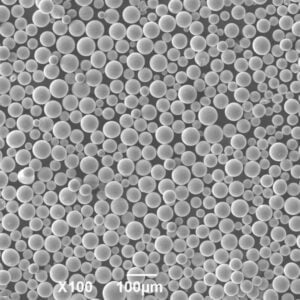
티타늄 분말의 응용 분야
The versatile properties of titanium powder enable unique applications in the following industries:
| 산업 | 신청 |
|---|---|
| 항공 우주 | Engine components, aircraft structures, space vehicles |
| 의학 (Yi-hak) | Implants, surgical instruments, medical devices |
| 자동차 | Connecting rods, valves, springs, fasteners |
| 화학적 | Corrosion resistant vessels, heat exchangers, pipes |
| Sporting goods | Golf clubs, tennis rackets, bicycles, helmets |
| 첨가제 조형 | Aerospace, automotive, and medical 3D printed parts |
Titanium’s biocompatibility makes it ideal for implants and medical devices. Its corrosion resistance suits it for seawater applications. The high strength is useful for critical components in aerospace.
티타늄 분말의 사양
Titanium powder is available in different size ranges, shapes, purity levels, and composition to suit specific applications.
| 파라미터 | 사양 |
|---|---|
| 입자 크기 | 15-45미크론, 45-105미크론, 105-250미크론 |
| 입자 형태 | Spherical, angular, mixed morphology |
| 순결 | Grade 1 (99.2% Ti), Grade 2 (99.5% Ti), Grade 4 (99.9% Ti) |
| Alloy grades | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-7Nb, Ti-64, Ti-1023 |
| 제작 방법 | Gas atomization, plasma atomization, hydride-dehydride |
The particle size distribution, morphology, oxygen/nitrogen content, and microstructure are controlled as per application requirements.
Suppliers of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder is supplied by leading metal powder manufacturers globally:
| 공급자 | 위치 |
|---|---|
| AMETEK | 미국 |
| AP&C | 캐나다 |
| TLS 테크닉 | 독일 |
| 테크나 | 캐나다 |
| 메탈리시스 | 영국 |
| 프락세어 | 미국 |
| 리오 틴토 | 캐나다 |
| ATI Powder Metals | 미국 |
| CNPC 파우더 그룹 | 중국 |
Titanium powder prices range from $50/kg to $500/kg based on purity, particle size, production method, and order volume. Custom alloys, special particle morphologies, and strict tolerances cost more.
Handling and Storage of Titanium Powder
Special precautions are needed when handling titanium powder to prevent fires, explosions, and property damage:
- Store in cool, dry, inert environments away from moisture, sparks, and flames
- Use conductive containers grounded to prevent static charge buildup
- Local exhaust ventilation is recommended to control dust
- Avoid dust accumulation to minimize explosion hazard
- Wear dust masks, safety goggles, gloves to prevent inhalation and skin contact
- Follow material safety data sheet (MSDS) instructions for safe handling
Inspection and Testing of Titanium Powder
Titanium powder batches are tested to ensure they meet the required material specifications:
| 시험 방법 | Parameter Measured |
|---|---|
| 체분석 | 입자크기 분포 |
| 레이저 회절 | Particle size distribution, mean size |
| 주사전자현미경 | Particle morphology, microstructure |
| 에너지 분산 X선 분광법 | 화학적 조성 |
| X선 회절 | Phase composition |
| Spectrophotometry | Oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen content |
| 탭 밀도 | Apparent density, flowability |
| Pycnometer | Skeletal density |
Sampling and testing as per ASTM standards ensures titanium powder quality for critical applications.
Comparing Titanium Powder to Alternatives
Titanium has advantages and disadvantages compared to substitute materials:
| 티타늄 (Titanium) | 알루미늄 | 스테인리스 스틸 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 밀도 | 낮음 | 더 낮게 | 높은 |
| 힘 | 높은 | 중간 | 높은 |
| 내식성 | 훌륭함 | 좋은 | 좋은 |
| 온도 저항 | 좋은 | 중간 | 더 나은 |
| 비용 | 높은 | 낮음 | 중간 |
| Magnetic permeability | 낮음 | 낮음 | 높은 |
| 생체적합성 | 훌륭함 | 가난 | 좋은 |
Titanium stands out for its corrosion resistance and biocompatibility despite its higher cost. Aluminum and stainless steel may be cheaper alternatives depending on application requirements.
Pros and Cons of Titanium Powder
| 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|
| 높은 강도-중량 비율 | Expensive compared to steels |
| 부식 방지 | Reactivity with oxygen at high temperatures |
| 무독성, 비알레르기성 | Low elastic modulus can mean springback in machining |
| 뛰어난 생체 적합성 | Low thermal conductivity |
| 고온에서도 특성 유지 | Requires inert atmosphere processing |
| Wide range of alloying possibilities | Limited high temperature strength |
Titanium powder enables lightweight, strong parts but requires controlled handling and processing. Cost is higher than conventional alloys.
Frequently Asked Questions about Titanium Powder
Here are answers to some common questions about titanium powder:
Q: What is titanium powder used for?
A: Titanium powder has uses across aerospace, medical, automotive, chemical, and sporting goods due to its high strength, low weight, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and biocompatibility. It is commonly used for critical rotating parts in aircraft engines, orthopedic implants, automotive components, heat exchangers, and additively manufactured parts.
Q: Is titanium powder safe to handle?
A: Titanium powder can ignite and explode when very finely divided and exposed to air. Proper grounding, inert atmosphere, ventilation, and protective equipment are essential when handling titanium powder. It is also non-toxic and hypoallergenic on skin contact.
Q: What is the difference between Grade 1 and Grade 5 titanium powder?
A: Grade 1 titanium powder has higher purity with lower oxygen and iron content compared to Grade 5. Grade 1 provides better corrosion resistance while Grade 5 offers higher strength. Grade 5 powder would be used where strength is critical while Grade 1 suits chemical resistance needs.
Q: Does titanium powder rust?
A: Titanium forms an impervious and self-repairing oxide layer that protects it from rusting and corrosion. It exhibits excellent corrosion resistance in most environments including saltwater. This property makes it suitable for marine applications.
Q: Is titanium powder magnetic?
A: No, titanium powder is non-magnetic. Its relative magnetic permeability is very close to 1 which makes it useful for non-magnetic applications instead of ferritic steels.
Q: What is the cost of titanium powder?
A: Titanium powder can range from $50/kg to $500/kg depending on purity, particle size, production method, morphology, and order volume. High purity grades suitable for medical use are more expensive. Custom alloys and special particle shapes also cost more.
Q: What is the difference between gas atomized and hydride-dehydride titanium powder?
A: Gas atomized titanium powder has a spherical morphology ideal for additive manufacturing while hydride-dehydride powder has an angular, irregular shape suited for pressing-and-sintering. The powder properties, surface chemistry, microstructure and cost differ for the two production methods.
Q: How is titanium powder produced?
A: The main production methods are gas atomization, plasma atomization, and hydride-dehydride process. Gas atomization using argon or nitrogen gas is a common method to produce fine spherical powder for AM. The hydride process generates angular powder for pressing into shapes before sintering. Plasma atomization can produce very fine spherical powders.
Q: What are the contents of a titanium powder material safety data sheet (MSDS)?
A: The MSDS will have health hazard information, reactivity data, toxicological data, handling precautions, storage information, spill procedures, firefighting instructions, first aid measures, and disposal guidelines. It is critical to review the MSDS before working with any amount of titanium powder.
Q: What standards apply to titanium powder?
A: Key standards include ASTM B833 for spherical titanium powder, ASTM B981 for titanium alloys for powder metallurgy, ASTM B988 for gas atomized titanium alloy powder, and ISO 22068 for additive manufacturing with titanium alloys. The specifications cover sampling, testing, size analysis, chemical analysis, and quality assurance.
"지금 바로 저희에게 연락하세요."
최신 제품 견적 및 재고 현황에 대한 문의는 저희에게 연락해 주세요.
