
A Comprehensive Guide to H13 Powder
Overview of H13 Powder H13 is a versatile chromium-molybdenum-vanadium hot work tool steel exhibiting very good resistance to thermal fatigue cracking and wear resistance. It has high hardness retention at elevated temperatures making it suitable for tools and dies used for hot forming, forging and casting applications. Key characteristics of H13 powder include: Excellent hot…
Small MOQ
Flexible sourcing for hundreds of products
Customization support
Customized powder according to industry
Rapid shipment
By DHL Express, safe and fast direct to your hands
Overview of H13 Powder
H13 is a versatile chromium-molybdenum-vanadium hot work tool steel exhibiting very good resistance to thermal fatigue cracking and wear resistance. It has high hardness retention at elevated temperatures making it suitable for tools and dies used for hot forming, forging and casting applications.
Key characteristics of H13 powder include:
- Excellent hot hardness and thermal fatigue resistance
- Good wear resistance and toughness
- High hardenability for increasing hardness through heat treatment
- Excellent machinability in annealed state
- Can be polished to fine surface finish
- Available in various size ranges and morphologies
H13 powder is used to produce hot work tooling needed across several industries including automotive, aerospace, mining, die-casting etc. This article provides a detailed overview of H13 powder.
Chemical Composition of H13 Powder
The typical chemical composition of H13 powder is:
| Element | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | Balance |
| Chromium (Cr) | 4.75-5.5% |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 1.1-1.75% |
| Vanadium (V) | 0.8-1.2% |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.2-0.6% |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.8-1.2% |
| Carbon (C) | 0.32-0.45% |
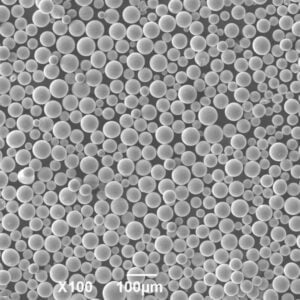
The key alloying elements like chromium, molybdenum and vanadium provide excellent heat resistance through formation of stable carbides.
Properties of H13 Powder
H13 powder possesses the following properties:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 7.3 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1420-1460¡«C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 24 W/mK |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.55 Ã×´Î.cm |
| Young’s Modulus | 200 GPa |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.29-0.30 |
| Tensile Strength | 1900 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 1650 MPa |
| Elongation | 8-9% |
| Hardness | 46-52 HRC |
H13 maintains its hardness, strength and thermal fatigue resistance up to 600¡«C making it an ideal choice for hot work tool and die applications.
Production Method for H13 Powder
The common production methods for H13 powder include:
- Gas Atomization?- High pressure inert gas used to atomize molten H13 alloy resulting in fine spherical powders with controlled size distribution.
- Water Atomization?- High velocity water jet impacts and disintegrates molten metal stream into fine irregular powders. Lower cost but higher oxygen pickup.
- Mechanical Alloying?- Ball milling of iron and alloying element powders followed by sintering and secondary atomization.
Gas atomization provides the best control over particle characteristics like size, shape and microcleanliness.
Applications of H13 Powder
Typical applications of H13 powder include:
- Additive Manufacturing?- Used in laser powder bed fusion and binder jetting to produce hot work tooling inserts, dies, blow molds etc.
- Thermal Spray Coatings?- Applied using wire/powder arc spray methods to provide wear and heat resistant coatings.
- Metal Injection Molding?- To manufacture small, complex hot work parts with tight tolerances like forging dies.
- Powder Metallurgy?- Press and sinter process to produce hot forming tools and dies cost effectively.
- Welding Filler?- Used as flux cored wire providing excellent resistance to heat and wear in the welded component.
Specifications of H13 Powder
H13 powder is available in various size ranges, shapes and grades including:
- Particle Size:?From 10-45 microns for AM methods, up to 150 microns for thermal spray processes.
- Morphology:?Spherical, irregular and blended particle shapes. Smooth spherical powder provides optimal flow.
- Grades:?Conforming to AISI, DIN, ASTM, and other equivalent standards. Custom alloys also available.
- Purity:?Oxygen content from 100-2000 ppm depending on production method. Lower oxygen levels offer better performance.
Global Suppliers of H13 Powder
Some of the major suppliers of H13 powder include:
- Sandvik Osprey (UK)
- Erasteel (France)
- HC Stark (Germany)
- Dura-Bar Metal Services (USA)
- Tekna Advanced Materials (Canada)
- CNPC Powder Group (China)
These companies produce H13 powder using various atomization techniques and customized alloys tailored for specific hot work tool and die applications across industries.
Pricing of H13 Powder
Pricing of H13 powder depends on several factors:
- Purity levels
- Particle size and morphology
- Powder production method
- Order volume
- Additional processing
- Supplier and geographical location
| Grade | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Commercial | $15-25 per kg |
| High purity | $25-50 per kg |
| Ultrafine | $50-120 per kg |
| Special grade | $120-250 per kg |
Gas atomized and high purity grades command much higher pricing than commercial H13 powder. Smaller quantities are also costlier.
Storage and Handling of H13 Powder
H13 powder requires the following controlled storage and handling:
- Store in sealed containers under humidity control to prevent oxidation
- Avoid fine powder accumulation to minimize dust explosion hazards
- Use proper grounding and PPE when handling powder
- Prevent contact with sparks, flames or ignition sources
- Follow recommended safety practices from supplier SDS
Inert gas glove box techniques are preferred for handling reactive alloy powders like H13.
Inspection and Testing of H13 Powder
Key quality control tests for H13 powder:
- Chemical analysis using OES or XRF to ensure correct composition
- Particle size distribution as per ASTM B822 standard
- Morphology analysis through SEM imaging
- Powder flow rate measured as per ASTM B213 standard
- Density determination by helium pycnometry
- Impurity testing by ICP-MS
- Microstructure characterization by X-ray diffraction
Thorough testing ensures uniform chemistry, physical characteristics and microstructure suitable for application requirements.
Comparison Between H13 and D2 Tool Steel Powders
H13 and D2 are two tool steel powders compared:
| Parameter | H13 | D2 |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Hot work steel | Cold work steel |
| Cr content | 4.75-5.5% | 11-13% |
| V content | 0.8-1.2% | 0.7-1.2% |
| Heat resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Wear resistance | Very good | Excellent |
| Toughness | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
H13 resists heat and thermal fatigue cracking whereas D2 offers very high wear resistance. H13 provides better toughness and lower cost.
H13 Powder FAQs
Q: How is H13 tool steel powder produced?
A: H13 powder is commercially produced using gas atomization, water atomization and mechanical alloying followed by sintering. Gas atomization offers the best control of powder characteristics.
Q: What are the main applications of H13 powder?
A: The major applications of H13 powder include additive manufacturing, thermal spray coatings, metal injection molding, and powder metallurgy hot work tooling requiring excellent heat and wear resistance.
Q: What is the recommended H13 powder size for binder jetting AM?
A: For binder jetting process, the typical H13 powder size range is 20-45 microns with spherical morphology to enable good powder packing and binder infiltration.
Q: Does H13 powder require any special handling precautions?
A: Yes, it is recommended to handle H13 powder carefully under controlled humidity and inert atmosphere using proper grounding, ventilation and PPE.
Q: Where can I purchase H13 powder suitable for hot forging dies?
A: For hot work die applications, high purity H13 powder can be purchased from leading manufacturers including Sandvik Osprey, Erasteel, HC Stark, and Dura-Bar Metal Services.
Contact us now
Please contact us for recent product quotes and stock availability.
